Treatment
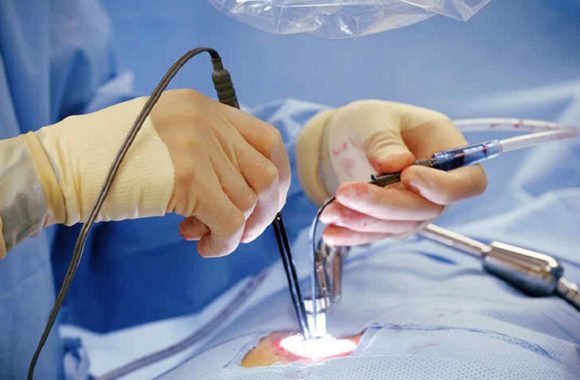
Surgery is often the last resort and is advised in patients who develop symptoms even after six weeks of conservative treatment, such as medications, injections, and physiotherapy. This surgery aims to remove the prolapsed part of the disc from the spinal cord
- A discectomy removes herniated disc material that compresses the spinal cord or a nerve root.
- Percutaneous discectomy is used for bulging discs or discs that have not extruded into the spinal canal.
- Laminotomy and laminectomy—'Laminotomy' removes a portion of the thin vertebrae, which produces a protective arch across the spinal cord (lamina). laminectomy involves removal of all the lamina on the selected vertebrae and may also remove thickened tissue that narrows the spinal canal depending on each patient.
- Minimally Invasive Spinal (MIS) Fusion – This spinal surgery is performed to replace the lamina and disc with the addition of the vertebra fusion graft. The anterior and posterior methods are used to perform the surgery. The most common procedure used is the posterior approach, where the procedure is performed from the back.